Data privacy legislation is a changing landscape. This article discusses three pieces of legislation – PIPEDA, CCPA, and GDPR and how they can impact your mission-critical JD Edwards systems. Six months from now, there are bound to be more. For instance, in the United States there are 13 states with data privacy legislation pending.
One thing to note, the GDPR represents the super set of data privacy legislation. If you meet GDPR requirements you will be compliant with CCPA and PIPEDA as well. Companies need to understand GDPR, data privacy, how to react with providers, and how the cloud impacts compliance.
As the heart of your enterprise IT system, your enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution houses large volumes of customer data that must be protected. And with the growth of data privacy legislation worldwide, personal data and information must be safeguarded. In addition, these regulations stipulate individuals have the right to consent on how their data is used.
A Quick, High-Level Overview of Data Privacy Legislation
The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA):
- Effective since April 2000
- Impacts all businesses doing business in Canada
- Required for any business that handles personal information
- Consumers have the right to know what data is being collected
- Consumers must give consent to use personal information
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA):
- Effective since January 2020
- Applies to all California residents
- Applies to any business that processes the personal data of California residents
- Only applies to companies with annual revenues of over $25M
- Consumers have the right to know what data is being collected and the right to be forgotten
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
- Effective since May 2018
- Applies to all individuals within the European Union and The European Economic Area
- Applies to any business that processes personal data of EU individuals
- Most rigid privacy and security law in the world
- Imposes an obligation on organizations anywhere in the world that target or collect data related to EU individuals
GDPR – General Data Protection Regulation
GDPR is the most challenging and most stringent privacy legislation globally and therefore is the most relevant for businesses to comply with. If you are compliant with GDPR, you will be in a good place regarding data privacy.
GDPR is made up of multiple articles that relate to various controls or compliances that are required. Note, not all the articles apply to JD Edwards or ERP. Therefore, from an organizational perspective you need to be concerned with all the articles, but not all the articles are relevant from an ERP perspective.
GDPR articles relevant to ERP include:
- Right of Access – Information on the controller and the stored personnel data must be protected
- Right of Erasure – Delete data if no longer required for the original purpose
- Right of Data Portability – Individuals can request copies of personal data
- Processor – Processing by third parties must be governed by contract
- Default Privacy by Design and by Default – Develop default privacy protection mechanisms and implement monitoring processes
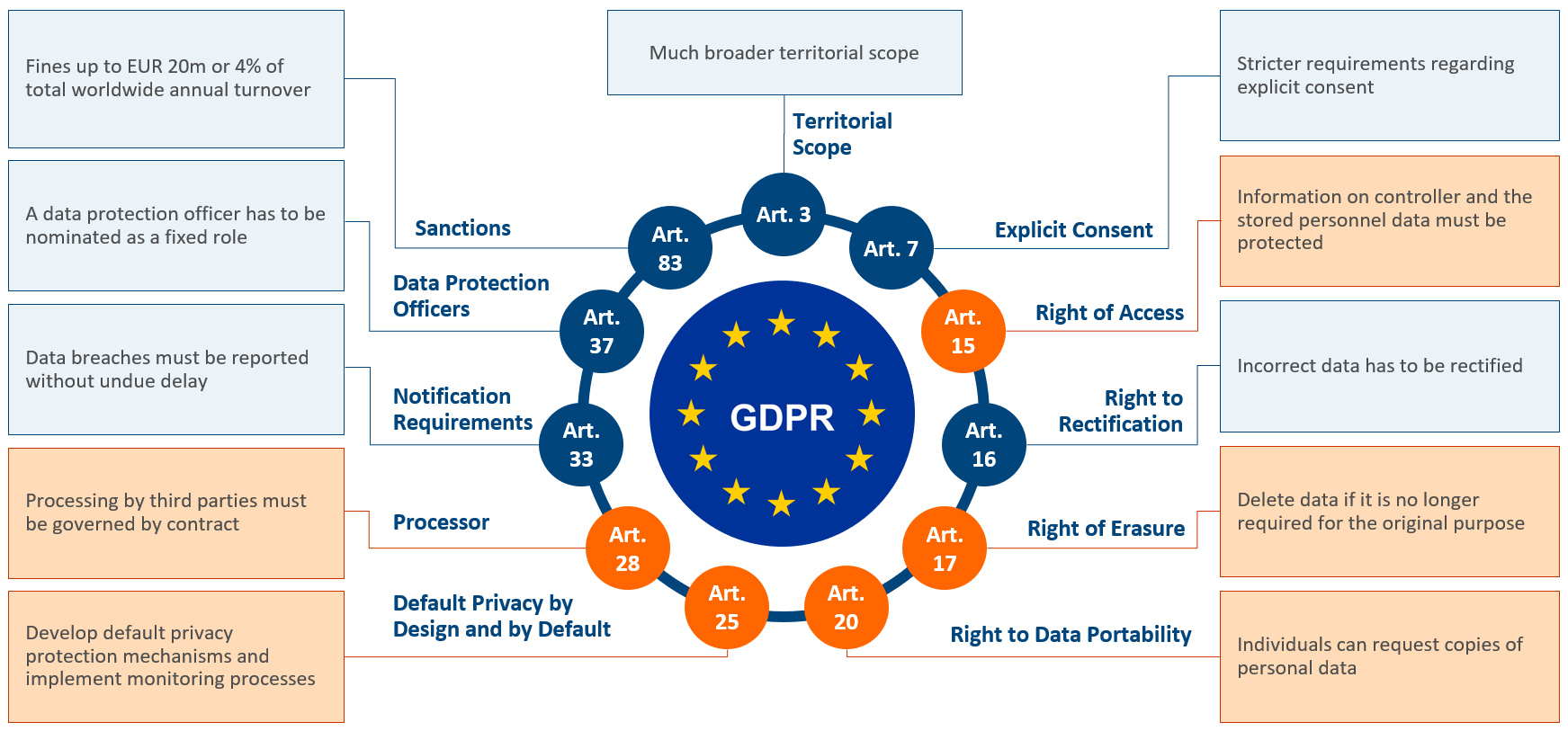
The GDPR Privacy Rights for Individuals
All data privacy regulations are designed to protect an individual’s data. GDPR is the most comprehensive and covers the following rights. These are the core issues and the foundation of today’s data privacy regulations.

Data Privacy and ERP
ERP systems like JD Edwards can hold a vast amount of personal customer data. Organizations should adopt a culture of responsible data management to protect the organization and the customer. Also, organizations should enact a privacy policy to ensure access to personal information is limited and is compliant with data privacy regulations.
Businesses often struggle with the “right to be forgotten” with their ERP systems. Companies must prove that every record of an individual’s data has been completely wiped. Regarding JD Edwards and ERP systems, this can be problematic, especially with system back-ups that can sometimes go back several years. This is a challenge that needs to be addressed in an organization’s compliance solution.
Personal Data and JD Edwards
Personal data is any information that can be used to identify a person.
There is no easy check box in JD Edwards to locate an individual’s data. You have to go and find it. Therefore, it can be subject to some interpretation.
Not all of these are standard to JD Edwards but depending on your business and the tools you use, below is some of the information you may need to protect.
- Home and work information
- Financial information
- Travel history
- Health information
- Religious beliefs
- Family demographic information
- Fingerprints or generic information
- Leisure activities and hobbies
- Behavioral patterns and interests
- Online behavioral patters
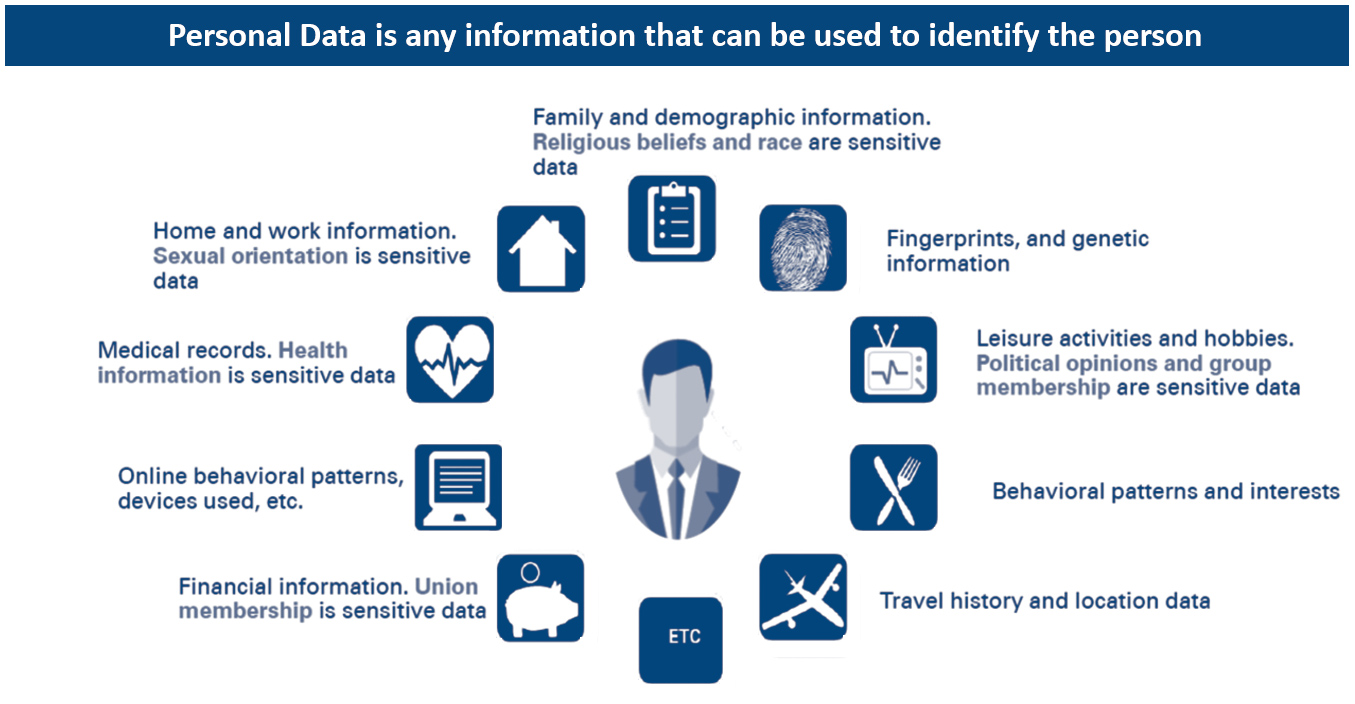
How to Find Personal Data in JD Edwards
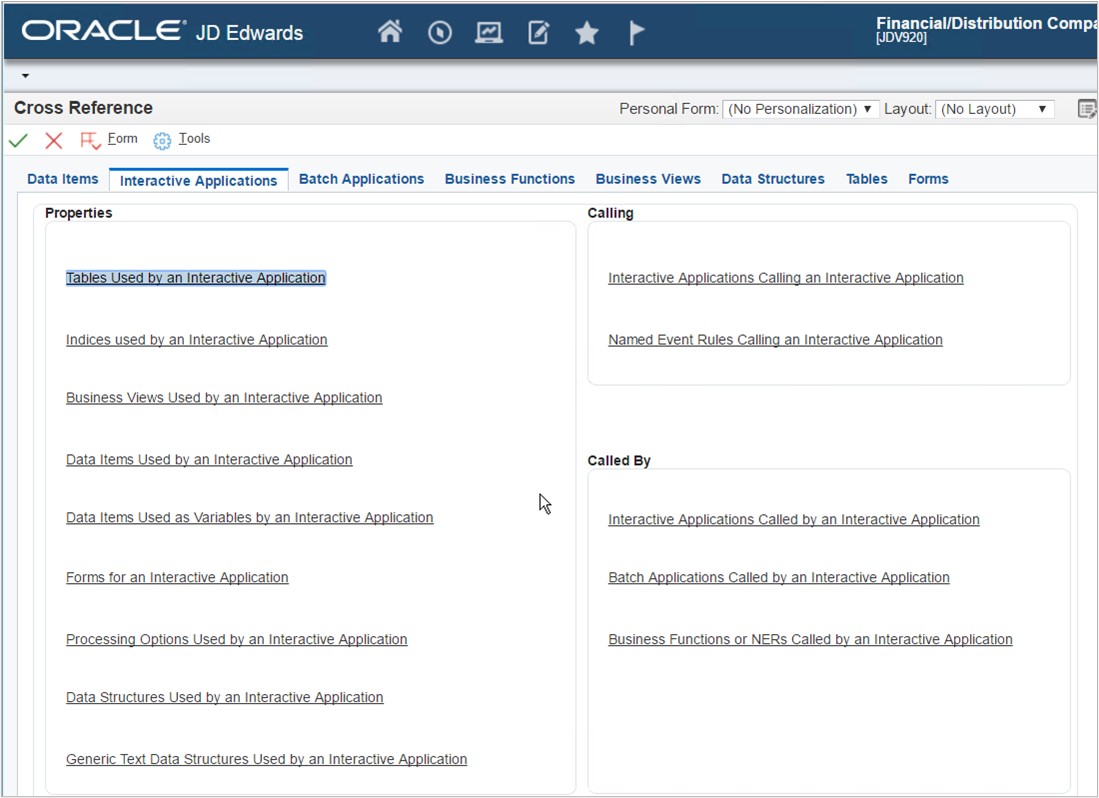
The JD Edwards Cross Reference Facility tool should always be built and always be available. It provides all the inter-relations between all the components in JD Edwards. For example, where social security, mailing information, or gender information is used throughout the system. The Cross Reference Facility tool is vital from a forensics perspective and from a development and administrative perspective to provide protection and compliance information.
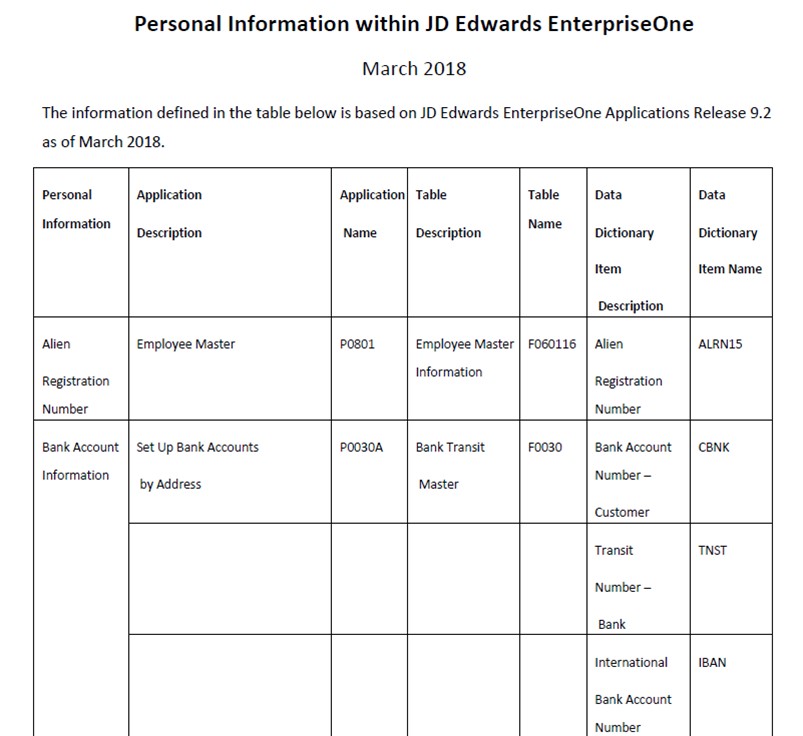
The JD Edwards Personal Information document (Doc ID 2388299.1) can also be helpful to identify personal information details. It determines which applications, tables, and data dictionary items manage and store customer, supplier, and employee personal information. Using these details, you can utilize the Cross Reference Facility tool to identify all locations in the system those data elements exist.
What is Data Protection?
Data protection is one of the critical tenets of GDPR and other data privacy regulations.
Under the terms of GDPR, you must have a Data Protection Officer named. It is the responsibility of this role to ensure data compliance. To provide sufficient data protection, you need effective data security management and a robust security strategy.
There are several tools within JD Edwards to enable a robust security strategy. These tools can help restrict what users can do and what they can see in the system. By limiting access and functionality, these tools enable more effective data protection.
Some of the JD Edwards object-based application security tools include:
Object Security Tools
- Applications Security
- Action Security
- Row Security
- Column Security
- Processing Option Security
- Tab Security
- Exit Security
- Exclusive Application Security
- External Calls
- Solution Explorer Security
- Data Browser
- Media Object
- Portal Security
- Published Business Services (BSSV)
- Data Selection Security
- Application Query Security
User Defined Objects (UDOs)
- E1 Pages
- Data Browser
- CafeOne
- Advanced Queries
- User Overrides
- Fast Path
- Solution Explorer
- OneView Reports
- Watch Lists
Other Security Tools
- Business Unit Security
- Password Security
- Data Privacy
- Data Change Tracker
- UDC Sharing
Getting Compliant
Compliance is not exciting. It’s a lot of paperwork. Through an in-depth analysis of GDPR requirements, Syntax identified over 100 points of concern. About 85% of these are contractual, while the remaining 15% are ERP security related.
Syntax recommends eight steps to measure your compliance and to identify gaps in compliance:
- Awareness and Communication: Ensure your employees understand GDPR and communicate with service and staff about why you are collecting the data
- Analysis of Personal Data: Analyze a list of all sensitive data you store and process
- Review Procedures: Have a suitable privacy policy in place and review it regularly
- Access Rights: List what access rights should be granted and how changes should be handled
- Customer Consent: Ensure your customers consent to you processing their data
- Data Breaches: Implement a procedure for handling data breaches
- Impact Assessments: Carry out a data protection impact assessment
- Data Protection Officers (DPO’s): Determine whether you need a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
Conclusion
Data privacy isn’t exciting, but it is imperative. Legislation is growing, and companies need to understand and be aware of data privacy regulations and how they will be impacted. These regulations are complicated and can involve severe penalties.
To learn more about JD Edwards, visit our JD Edwards insights page, where you can access JDE whitepapers, webinars, data sheets, and much more.
Learn more from the experts at Syntax and Q Software. View the on-demand webinar, The Impacts of Data Privacy Regulations on JD Edwards EnterpriseOne.

